Allergies, often dismissed as minor inconveniences, can be significant disruptors to one’s quality of life. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify allergies, provide insights into allergy prevention, and offer practical insights into their understanding, management, and achieving a fulfilling life while living with them.
I. Introduction
Allergies, affecting millions globally, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Allergy prevention is crucial in mitigating these effects, involving a proactive approach to identifying triggers, implementing lifestyle changes, and seeking appropriate medical advice. By understanding and practicing effective allergy prevention strategies, individuals can lead healthier, more comfortable lives free from the disruptive symptoms of allergies.
II. Understanding Allergies
a. Defining Allergies
At their core, allergies are hypersensitive responses of the immune system to substances that are otherwise harmless. These substances, known as allergens, provoke an immune reaction, leading to various symptoms.
b. The Role of the Immune System
To grasp allergies fully, we must first appreciate the immune system’s primary role in protecting the body. However, in the context of allergy prevention, the immune system mistakenly identifies innocuous substances as threats, setting off a cascade of reactions.
c. Importance of Allergy Prevention
III. Types of Allergies
Allergies don’t conform to a one-size-fits-all model. They manifest in various forms, each with its unique characteristics.
a. Food Allergies
Food allergies can trigger a range of symptoms, from hives and digestive issues to severe anaphylaxis, and identifying the culprits is essential.
b. Seasonal Allergies
Pollen and other airborne allergens can wreak havoc on those with seasonal allergies. Understanding the seasonal patterns and allergen sources is the first step toward relief.
c. Allergic Skin Conditions
Eczema and hives are just two examples of skin conditions induced by allergies. Discover how to manage and soothe these often uncomfortable symptoms.
d. Allergic Asthma
Allergies can exacerbate asthma, leading to more frequent and severe attacks. Learn how to control allergic triggers to breathe easier.
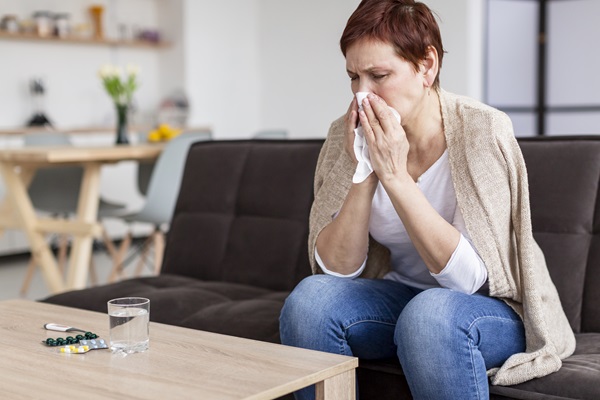

IV. Common Allergens
To navigate allergies effectively, it’s crucial to identify the usual suspects.
a. Pollen
Pollen allergies are prevalent, especially in the spring and fall. Recognizing pollen sources and monitoring local pollen counts can help.
b. Dust Mites
Dust mites, tiny creatures living in our homes, are a common allergen. Implementing proper cleaning measures is key to reducing exposure.
c. Pet Dander
Pet allergies, often triggered by proteins in an animal’s skin cells, are a challenge for pet owners. Discover strategies to coexist with your furry friends.
d. Insect Stings
Insect venom can incite severe allergic reactions in some individuals. Know how to avoid stings and what to do in case of a severe reaction.
e. Allergens
Allergic reactions to foods can range from mild to life-threatening. Learning to recognize allergens in ingredient lists is a survival skill for those with food allergies.
V. Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions vary widely in their severity and onset time, which necessitates a nuanced understanding.
a. Immediate and Delayed Reactions
Some allergic reactions occur within seconds of exposure, while others may take hours or even days to manifest.
b. Severity Levels
Understanding the varying degrees of allergic reactions, from mild to anaphylactic, is critical for both self-management and effective communication with healthcare providers.
VI. Diagnosing Allergies
a. The Allergy Testing Process
The journey to allergy management begins with diagnosis, which often involves several testing methods.
b. Skin Prick Tests
Skin prick tests are a common method for identifying allergies. They involve introducing tiny amounts of allergens under the skin to gauge the body’s reaction.
c. Blood Tests (IgE)
Measuring specific antibodies in the blood, particularly Immunoglobulin E (IgE), can reveal sensitivities to various allergens.
d. Elimination Diets
For food allergies, elimination diets can be an effective strategy for allergy prevention. This method involves systematically removing and reintroducing specific foods to observe their impact, helping to pinpoint and avoid problem foods.
e. Consultation with Allergists
Allergists are pivotal in the diagnosis process, as they conduct comprehensive assessments.
f. Allergy History
Detailed discussions of an individual’s allergy history are essential to understanding the scope of their condition.
g. Physical Examinations
Physical examinations help allergists identify potential allergen sources and assess the impact of allergies on the patient’s well-being.
h. Testing Recommendations
Based on the patient’s history and examination, allergists recommend suitable tests and subsequent management plans.
VII. Managing Allergies
a. Medications
Various medications play a crucial role in allergy prevention, providing relief from symptoms and helping to manage allergic reactions effectively.
b. Antihistamines
Antihistamines work by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released during allergic reactions, thereby reducing symptoms like itching and sneezing.
c. Decongestants
Decongestants can relieve nasal congestion, a common symptom in allergies, by narrowing blood vessels in the nasal passages.
d. Steroids
In cases of severe inflammation, steroids may be prescribed to reduce swelling and discomfort.
e. Epinephrine
Epinephrine, often carried by those with severe allergies, is a life-saving injection used to counteract severe anaphylactic reactions.
f. Immunotherapy
For long-term relief, some opt for immunotherapy.
g. Allergy Shots
Allergy shots, or allergen immunotherapy, involve regular injections of allergens to desensitize the immune system.
h. Sublingual Immunotherapy
This alternative to shots entails placing allergen extracts under the tongue to achieve a similar desensitizing effect.
i. Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly impact allergy management.
j. Allergen Avoidance
Learning to identify and avoid allergens is fundamental to minimizing exposure.
k. Clean Living Spaces
Reducing allergens in the home through regular cleaning and minimizing dust can ease symptoms.
l. Dietary Adjustments
For food allergies, dietary modifications are necessary. Understanding food labels and cross-contamination risks is crucial.
m. Emergency Preparedness
In severe cases, emergency preparedness is a must.
n. Anaphylaxis Action Plan
Individuals with severe allergies should have an anaphylaxis action plan, detailing steps to take in case of a severe reaction.
o. Carrying Epinephrine
Carrying an epinephrine auto-injector is a literal lifesaver for those at risk of anaphylaxis.
VIII. Living Well with Allergies
a. Education and Awareness
Education and awareness are vital components of allergy prevention, empowering individuals to recognize triggers, read labels, and spread knowledge about managing allergies effectively.
b. Support Systems
Support, whether from family, friends, or organized groups, is invaluable.
c. Family and Friends
Family and Friends play a crucial role in allergy prevention by understanding and supporting individuals with allergies. Their awareness and assistance can significantly contribute to a safer environment and improved quality of life.
d. Allergy Support Groups
Joining allergy support groups is beneficial for individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge about allergy prevention, share experiences, and gain practical insights into managing allergies effectively.
e. Traveling with Allergies
Travel can be a challenging terrain for those with allergies.
f. Preparing for Trips
Planning, from accommodations to meals, is essential to ensure a safe journey.
g. Dining Out Safely
Eating out can be tricky, but with the right precautions and communication, it’s possible to enjoy a meal without worry.
h. Psychological Well-being
Emotional well-being is an often overlooked but critical aspect of allergy management.
i. Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies is crucial for managing allergies and promoting allergy prevention.
j. Stress Management
Managing stress effectively is essential for individuals aiming for allergy prevention. Techniques such as mindfulness, regular exercise, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle can help reduce the body’s susceptibility to allergic reactions
X. Conclusion
Allergies are not insurmountable obstacles. With knowledge, effective management, and a robust support system, it’s entirely possible to lead a fulfilling life while successfully managing allergies.