Inflammation, a natural response to injury or infection, can become harmful when it persists chronically, leading to health issues like heart disease and diabetes. Understanding how inflammation impacts your health is crucial for managing it effectively. Incorporating foods with anti-inflammatory properties into your diet can help combat this persistent inflammation and promote overall well-being.
I. Introduction
A. Understanding Inflammation and Its Impact on Health
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury and infection. While acute inflammation is a protective mechanism that helps heal wounds and fight infections, chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. Chronic inflammation can be triggered by various factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, and environmental toxins.
B. Importance of an Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Foods with anti-inflammatory properties are crucial for managing and preventing chronic inflammation. It involves consuming foods that reduce inflammatory markers while avoiding those that contribute to inflammation. This type of diet not only helps in managing existing health conditions but also promotes overall well-being and longevity.
C. Objectives of the Article: Highlighting Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods
This article aims to highlight the top ten anti-inflammatory foods that can be easily incorporated into your diet. By understanding the benefits and ways to use these foods, you can take proactive steps toward improving your health and reducing inflammation.
II. The Role of Diet in Inflammation
A. How Foods with Anti-Inflammatory Properties Contribute to Inflammation
Certain foods, particularly those high in refined sugars, trans fats, and processed ingredients, can trigger inflammatory responses in the body. For example, sugary beverages, fried foods, and processed meats are known to increase levels of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP).
B. Benefits of Foods with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Foods with anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve digestion, enhance mood, and support overall health. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, you can decrease inflammation and promote a balanced immune response.
C. Overview of Key Nutrients in Foods with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Key nutrients in foods with anti-inflammatory properties include omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, polyphenols, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients help combat oxidative stress, regulate immune function, and reduce the production of pro-inflammatory molecules.
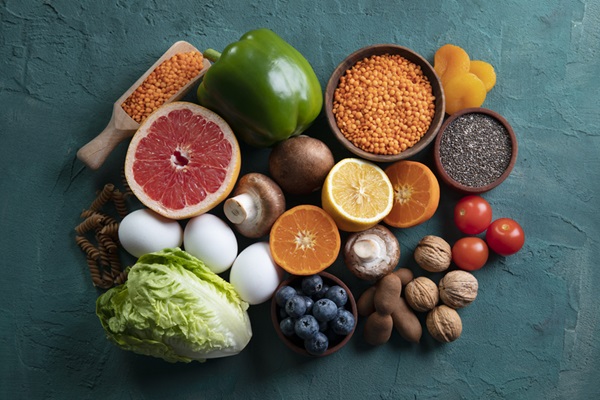

III. Top 10 Foods with Anti-inflammatory Properties
1. Turmeric
a. Active Compound: Curcumin
Turmeric is a vibrant yellow spice commonly used in Indian cuisine. Its active compound, curcumin, has powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Curcumin inhibits the activity of inflammatory enzymes and cytokines, making it a potent anti-inflammatory agent.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Turmeric
Turmeric can help reduce inflammation, improve brain function, lower the risk of heart disease, and alleviate symptoms of arthritis. You can incorporate turmeric into your diet by adding it to curries, soups, smoothies, or golden milk lattes. For enhanced absorption, combine turmeric with black pepper and healthy fats.
2. Blueberries
a. Rich in Antioxidants and Phytochemicals
Blueberries are packed with antioxidants and phytochemicals, including anthocyanins, which give them their deep blue color. These compounds help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Blueberries
Regular consumption of blueberries can improve cognitive function, support heart health, and enhance immune response. Enjoy blueberries by adding them to yogurt, oatmeal, salads, or smoothies. They also make a delicious and nutritious snack on their own.
3. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines)
a. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). These fatty acids have strong anti-inflammatory effects and help regulate the body’s inflammatory response.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Fatty Fish
Omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish can reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, and improve mental health. Incorporate fatty fish into your diet by grilling, baking, or broiling it. Aim to consume at least two servings of fatty fish per week.
4. Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale)
a. Vitamins and Antioxidants
Leafy greens like spinach and kale are loaded with vitamins A, C, E, and K, as well as antioxidants and fiber. These nutrients help combat inflammation and support overall health.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Leafy Greens
Consuming leafy greens can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve digestive health, and support immune function. Add leafy greens to salads, smoothies, soups, or stir-fries. They can also be used as a nutrient-dense base for your meals.
5. Nuts and Seeds (Walnuts, Chia Seeds, Flaxseeds)
a. Healthy Fats and Fiber
Nuts and seeds, such as walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds, are excellent sources of healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. They help reduce inflammation and support heart health.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Nuts and Seeds
Regular consumption of nuts and seeds can lower cholesterol levels, improve gut health, and reduce inflammation. Add them to yogurt, oatmeal, salads, or smoothies. They also make a convenient and nutritious snack.
6. Olive Oil
a. Monounsaturated Fats and Polyphenols
Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and polyphenols, which have anti-inflammatory properties. The primary polyphenol in olive oil, oleocanthal, has been shown to reduce inflammation in a manner similar to ibuprofen.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Olive Oil
Using olive oil as your primary cooking oil can reduce the risk of heart disease, improve brain function, and support overall health. Drizzle olive oil over salads and vegetables, or use it as a base for cooking.
7. Tomatoes
a. Lycopene and Vitamins
Tomatoes are a rich source of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties. They also contain vitamins C and E, which help combat inflammation.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Tomatoes
Eating tomatoes can lower the risk of chronic diseases, improve skin health, and support heart health. Add tomatoes to salads, sauces, soups, or enjoy them fresh. Cooking tomatoes enhances the bioavailability of lycopene.
8. Garlic
a. Allicin and Anti-Inflammatory Compounds
Garlic contains allicin, an anti-inflammatory compound that helps reduce inflammation and boost immune function. Garlic also has antimicrobial properties.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Garlic
Regular consumption of garlic can reduce the risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, and support immune health. Add garlic to your dishes by mincing, crushing, or roasting it. It can enhance the flavor of various savory dishes.
9. Ginger
a. Gingerol and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Ginger contains gingerol, a bioactive compound with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Ginger helps reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Ginger
Ginger can help alleviate nausea, reduce muscle pain, and lower inflammation. Incorporate ginger into your diet by adding it to teas, smoothies, stir-fries, or baked goods. Fresh, powdered, or dried ginger can be used in various recipes.
10. Green Tea
a. Polyphenols and Antioxidants
Green tea is rich in polyphenols and antioxidants, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has strong anti-inflammatory effects. Green tea helps reduce oxidative stress and inflammation.
b. Health Benefits and Ways to Incorporate Green Tea
Drinking green tea regularly can improve brain function, support heart health, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Enjoy green tea as a hot or iced beverage. Matcha, a powdered form of green tea, can also be added to smoothies or baked goods.
IV. Practical Tips for Incorporating Anti-Inflammatory Foods
A. Meal Planning and Preparation
Planning your meals in advance can help ensure you include foods with anti-inflammatory properties in your diet. Create a weekly meal plan that features a variety of the highlighted foods and make a shopping list to keep you on track.
B. Recipes and Cooking Ideas
Experiment with new recipes that incorporate foods with anti-inflammatory properties. Try making a turmeric-spiced lentil soup, a blueberry and walnut salad, or a salmon and spinach stir-fry. Cooking at home allows you to control the ingredients and maximize the nutritional benefits.
C. Tips for Consistent Consumption
To consistently consume foods with anti-inflammatory properties, keep them readily available in your kitchen. Stock up on fresh produce, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils. Incorporate these foods into your daily meals and snacks to make them a regular part of your diet.

V. Additional Lifestyle Tips for Reducing Inflammation
A. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming.
B. Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation. Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
C. Importance of Adequate Sleep
Getting adequate sleep is essential for reducing inflammation and supporting overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep routine and create a restful sleep environment to improve sleep quality.
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the Benefits of Foods With Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Foods with anti-inflammatory properties can significantly improve your health by reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving digestion, enhancing mood, and supporting overall well-being.
B. Encouragement to Incorporate Foods with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
By incorporating the top ten foods with anti-inflammatory properties into your diet, you can take proactive steps towards reducing inflammation and improving your health. These foods are not only nutritious but also delicious and versatile.
C. Final Thoughts on Long-Term Health and Wellness
Embracing foods with anti-inflammatory properties and lifestyle can lead to long-term health and wellness. Make gradual changes to your diet and habits, and remember that consistency is key. Prioritize whole, nutrient-dense foods, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep to support your journey towards optimal health.

